Lessons from Django
I already have experience with the MVC paradigm through previous websites I've built with Django, Flask, and FastAPI.
- .NET supports hot reload from v6.0
Razor Scaffolds vs Django Templates
- Razor Pages: HTML template page with associated C#
- Layouts: The layout page controls the layout of each page
- Imports HTML, Javascript and StyleSheets
- Rendered where
@RenderBody()is called - Layout property is set in
Pages/_ViewStart.cshtml
- Partials:
- Templates:
- Tag Helpers: Enable server-side code to render HTML. Denoted by the
@prefix in the.cshtmlfile
- Layouts: The layout page controls the layout of each page
- cshtml files : Markup engine language for the razor engine used to render serverside HTML pages. Consider these the equivalent to template files in Django or Jinja2.
- cshtml.cs files:
@pageand@model YourApp.Pages.YourFolder.YourPagedirectives transition html to razor page@page: Can pass in route params@model YourApp.Pages.YourFolder.YourPagespecifies the type of model that is passed to the page
@RenderBody: placeholder where all the page-specific views show up, wrapped in the layout page@{...}: The{and}characters enclose a block of c# code- Can iterate using forloops using
@for- for loops can iterate over data in the ViewData directory. HTML elements are implicitly returned
- Can iterate using forloops using
- The
ViewDatadictionary : K/V store that passes data to the view @namespaceSet the namespace in the template- Should I structure namespace based on file structure?
Razor Page Models
Implementation of the Page Controller pattern, where there is a one-to-one mapping between pages and their controllers
public IActionResult OnGet(): Initializes state for the pagepublic async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync: Run when the page posts form dataPage()method: Creates aPageResultobject that renders the.cshtmlpage
Nuget vs pip requirements.txt package managers
- Make sure to install versions that are compatible with your dependencies (e.g. .NET version, C# version, etc.)
Models and migrations
Data Annotations: We can apply data annotations to model fields using attributes in the form of [Annotation] DataType varName
- Validation with Data Annotation Validators
- Example validators include:
[Required],[StringLength],[RegularExpression],[Range]
- Example validators include:
[Display]attribute: Specifies display name of a field[DataType]attribute: Specifies the type of data
Migrations
# goto Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console
# run in shell: InitialCreate is the name of our first migration. Change the name to whatever the name of your migration will be
Add-Migration InitialCreate
Update-Database
Data context : entry point for the LINQ to SQL framework.
How to set database connections?
- Use
ConnectionStringsinappsettings.json
Databases
LocalDB: Lightweight user-mode database for dev environment SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX):
- Equivalent to admin console in Django
- Hotkey:
Ctrl + \+Ctrl + SLINQ Queries: - LINQ queries are lazily evaluated
- Can construct lambda expressions on LINQ queries such as conditional filters
How to relate the following to transactions?
- Db Context:
- EntityState
context.Entry(...).State
Atomic Operations
We need to ensure atomic database operations to prevent race conditions
Pessimistic concurrency: Use database locks to prevent concurrency conflicts
- con: Complex to implement, performance degrades as users increase Optimistic concurrency: Allows concurrency conflicts to happen, then reacts to rectify them
- Types of error recovery include:
- Store-Wins scenario: Data store values take precendence and user is given an error on conflict
- Client-Wins / Last-In-Wins: Final write overwrites the preceeding writes
- Managing state for each transaction and db column: Unpractical to implement due to requirement of managing too much state
- How are conflicts detected?
- Concurrency token: Property that tracks queries and emits a conflict on update or delete during
SaveChanges()- Operation can complete if the values match, otherwise throw a
DbUpdateConcurrencyException
- Operation can complete if the values match, otherwise throw a
- Concurrency token: Property that tracks queries and emits a conflict on update or delete during
Atomic workflow using Optimistic Concurrency:
Async Methods:
- Async methods are the default for .NET Core and EF Core
- Database action statements are executed asynchronously (not the lazily evaluated operations)
- EF Core context is not thread safe
- Verify library packages use async if they call EF Core methods that send queries to the db
Entity Framework
I am putting model attribute conditions in the models section of the MVC WebAPI page
Entity Framework Core is an ORM for the .NET Core ecosystem
- Use cases include:
- Handling network connections and intermediate data
- Generates SQL and maps data back to POCO (plain old CLR object)
- Abstraction to allow LINQ queries to work on databases
Ideas in EF Core:
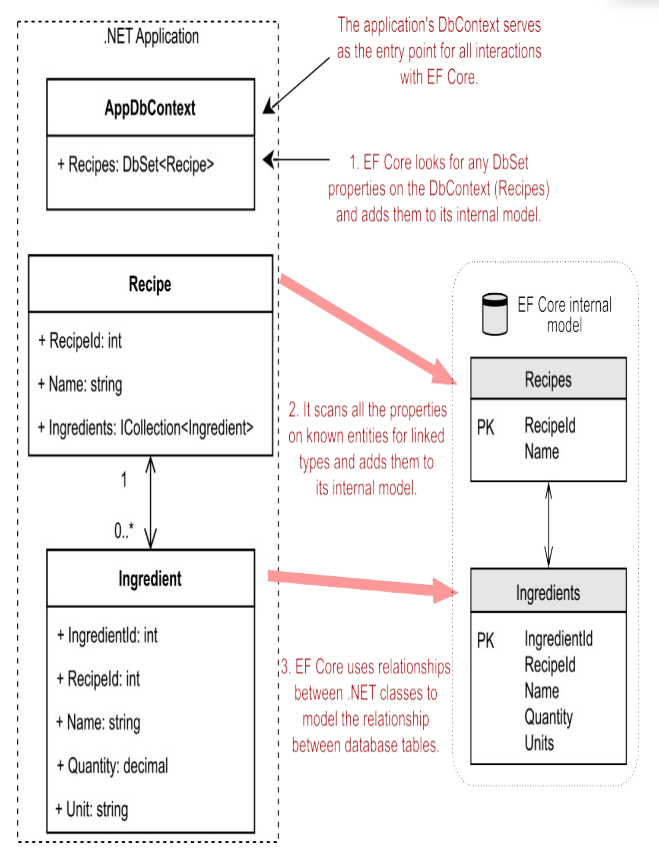
Entity: .NET class mapped by EF core to the database
Database Context:
DbContextused to configure EF core and access the database at runtime- Can have multiple
DbContext(s) and integrate with different databases in one application
- Can have multiple
DbSetproperties on theDbContextare added to the internal model --> Presents the collection of all entities in the context- So you don't have to manually add every entity to the model using
DbSetas it finds them based on relationships between entities. However, it's best practice to expose a DbSet for each entity if you want to query on them.
- So you don't have to manually add every entity to the model using
Visual studio makes creating CRUD APIs very easy. Just define a model then create a scaffold item to controller
- Default CRUD create scaffold is vulnerable to overposting (changing form inputs to post to fields that should not be updated)
- Use
TryUpdateModelAsyncto stop overposting on Edit - In MVC -->
Bindattribute prevents overposting on create by limiting postable fields- Note that BIND clears out existing fields that are not bound, so the
TryUpdateModel-->SaveChangesmethod is recommended for edits
- Note that BIND clears out existing fields that are not bound, so the
Entity States: What records should be updated on SaveChanges()
Addedstate: Mapped to INSERTUnchangedstate: starting stateModifiedstate: Mapped to UPDATEDeletedstate: Mapped to DELETEDetachedstate: Isn't tracked by db context
Authentication
- TODO: Token based
- Authentication overview
Input Validation
Sanitization
Validate argument against expected format
Handling errors appropriately (see exceptions section)
Exceptions
HTTP default status codes Types of errors:
- Upstream errors
- Validation errors
- Business logic errors
- 500 errors
Testing
Integration testing --> We write these
Performance Monitoring
Should I use the same techniques?
Documentation
Plan is to currently add it in the docs repository
Security
- TODO:
OData and REST API spec
- TODO: I don't really know what OData is trying to achieve? Standardised REST?
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/odata/webapi-8/getting-started?tabs=net60%2Cvisual-studio-2022%2Cvisual-studio
Logging
- Specify in
appsettings.{Environment}.json - Cloud telemetry in Azure