HTML
Reviewing HTML to make an awesome animated webpage
https://web.dev/learn/html/overview/ https://isobar-us.github.io/code-standards/
Isobar Frontend Code Standards for HTML
Goals for markup
- Maintain a clear separation o concerns, avoid in-line styles and in-line javascript whenever possible
- Build pages as a library of components, in such a way that blocks of code can be broken up and reused when implemented
- Use the most meaningful yet minimal markup to complete deliverables
- Have a reference implementation that each contributor knows what sort of structures are appropriate
Before getting started:
- Discuss the final delivery environment (mobile, desktop, etc)
- Templates and types of pages
- Which sections are reusable, which are managed by software vs by-hand
- Framewords, CSS grid systems
- Server-side delivery platforms
What are the best practices?
- Use semantic markup when possible
- Use the latest HTML5 markup specifications from W3C
- Include the proper doctype to trigger standards mode (
<!doctype html>for html5) - Define character encoding
<meta charset="UTF-8"> - Use all open and closing elements nested in the correct ways to maximum compatibility and clarity of document structure
- Valdiate your markup
- Use indentation appropriately
- Use quotes to surround all attribute values in HTML, despite quotes being optional in HTML5
- Use semantic names over descriptive names in
idandclassattributes- E.G. "secondary-nav" is better than "left-nav"
- All links should point to absolute or relative URLs with user-readable content. Don't link to XML or JSON designed to be AJAX'd with JS
- Use enclosed
<p>tags to separate paragraphs instead of<br> - Use definition lists
<dl>to display a single record of name-value pairs - Only use tables for tabular data, not page layout
- Make full use of the
<form>tag for all sections requiring use input
Next Steps:
- Site maintenance procedures
- Browser testing strategies
- How new features will be added
- Where new features will be added
- What the file system looks like for static site assets
- If a CDN is involved
- Naming conventions and organization of graphics and photography assets
- If the "back-end implementation" of static HTML templates will require review by front-end team members
Frontend Terminology
Polyfill: Piece of JS code that provides modern functionality in older browsers that do not natively support it
Elements
Elements: Content nested between the opening and closing tags
- Tag name is the content in the brackets
Types of elements:
- Non-Replaced: Have opening and optional closing tags that surround them. May include text, other tags as sub-elements
- Replaced: Can be replaced by options (such as a UI widget), image file or raster.
- Void element: Self closing tags, often denoted by
<tag />- Most replaced elements are void elements but not all
Tags have attributes which define the behaviour, linkage and functionality of elements
- Most attributes are name/value pairs
- XHTML style markup: Style to use lowercase letters for all element and attribute names, self-closing empty elements
Default appearance of semantic elements is set by user-agent stylesheets
- Semantic means "relating to meaning"
- Semantics of an element is important for search engines and assistive technologies
- Different browsers may have different user-agent stylesheets (elements may be rendered differently between browsers)
Document Object Model (DOM)
Nodes: Javascript object is created by the browser for each element and section of text encountered
HTML DOM API: Access and control each HTML element via the DOM
- HTMLElement interface: represents HTML element and all descendent nodes
Document Structure
<!DOCTYPE html>doctype tells the browser to use standards mode<html>Root elementlangattribute: main ISO language + region
- Head Element
<head>: Contains metadata such as search engine info, social media, icons, mobile screen shortcut, behaviour of the sitecharsetattribute: encoding<title><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />: Viewport metadata.- Above example makes the content the width of the screen
- Including CSS
- Use
<link>with arel="stylesheet"attribute,<style>to add css directly or thestyleattribute - Styles should go in the head because you want the browser to know how to render the content when it is loaded (prevents unnecessary repainting)
- Use
- Favicon using
<link rel="icon" ...> - Alternate versions for different languages
<link rel="alternate">- For the authoritative source code use
<link rel="canonical"
- For the authoritative source code use
<base target="_top" href="...">sets the default link URL and target- Target: Where the links should open --> e.g. new window or new tab
<script>tag Used to include scripts- Defaults to Javascript
- Note: with JS, don't reference elements before they are created --> put scripts at the bottom of the
<body>element if they reference other elements. - JS elements are render-blocking, and the browser stops downloading all assets when scripts are downloaded and doesn't resume until execution has completed
- Can modify this behaviour with
deferandasync
- Can modify this behaviour with
<link>: Link to fragment, url or downloadable resource- Download with
href="blob:downloadUrl" download="outputFilename" targetattribute:_self: open link in current window_parent: link nested in a parent object or iframe_blank: open link in new tab_top: top most ancestor
- Can track link clicks using the
pingattribute to ping a url on click - Tips for using Links
- Provide enough information about the linked resource so the user knows what they're clicking on
- Ensure links are different from regular text
- use focus styles to enable keyboard navigators to know where they are when tabbing
- Content between opening
<a>and closing</a>is the default accessible name - Interactive content should not go in links (bad UX when loading)
- Download with
Metadata
<meta>tag represents metadata that cannot be represented by<title>,<link>,<script>,<style>, and the lesser used<base>in the<head>element- Required tags are charset and viewport
- Attributes in meta tag
<meta name="attribute" content="">:http-equivattribute in a<meta>tag:- Has value as pragma directive which describes how a page should be parsed
- most common value is refresh which sets timeout until page refresh
descriptionattribute: used in SEOrobotsattribute: tells bots to not index the site and follow linkstheme-colorattribute:- Open graph: Controls how social media sites display your content
- Specific social media sites may have their own similar syntaxes like Twitter (now X?)
- Manifest file: Prevent unwieldy header of many link and meta tags by defining them in a manifest file
Semantic HTML
Using the correct HTML elements for your content
- Accessibility object model (AOM)
roleattribute: describes the role of an element in the context of the document- Semantic elements have implicit roles (such as header, main, footer as landmarks)
- Role names are used to build the AOM
Landmarks: <header>, <nav>, <main>, <aside>, <section>, <footer>
- Use landmarks over roles or divs which improves the clarity of the document structure
<header>: has the banner role if the header is top-level otherwise a section header- Best to put your title, logo and main navigation here
<nav>: identifies content as navigation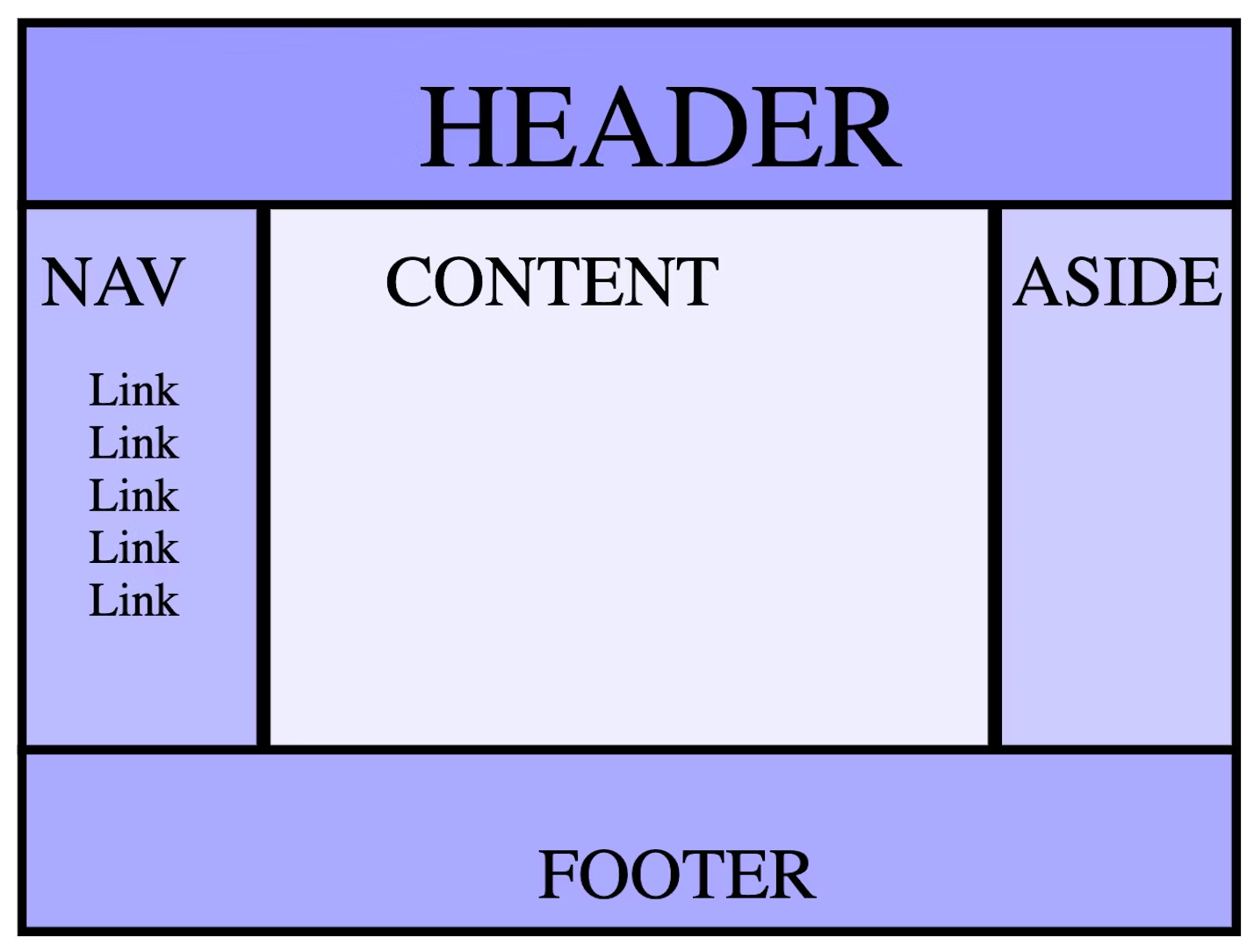
Attributes
Boolean, enumerated and global attributes
- Global attributes:
id: Unique identifier that:- Target of a link's fragment identifier (goto fragment in page denoted by #id)
- Identify an element for scripting
document.getElementById - Associate a form element with its label using the
forattribute - Providing a label or description for assistive technologies
- Targetting styles in CSS (attribute selector)
class: Additional way of targetting elements with CSS and JS, but is not used by HTMLaria-*: Accessibility propertiesstyle: styletabindex: Recieve focus via tab key pressrole: Part of ARIA spec covered earliercontenteditable
- Custom Attributes: Create custom attributes by adding the
data-prefix
Text
Use aria-labelledby to turn headings into regions for accessibility
Quotes and citations: Use <blockquote>, <q> and <cite>
citeattribute that is not readable to the user
HTML Entities: There are four reserved entities in HTML: <, >, &, and ". Their character references are <, >, & and " respectively.
- Symbols like © and ™ are useful
Navigation
<nav>element: Informs navigation block- Skip Link: Skip to the main content of the site when hitting tab
- Hide content in the non-focused and non-active state using the selector
.visually-hidden:not(:focus):not(:active) - Link text should be "skip to main" as the accessible name
- Hide content in the non-focused and non-active state using the selector
- Table of contents: Make sure to wrap these lists in a
<nav>element with anaria-labelledbyattribute description - Breadcrumbs: Provides links to each previous page a user has navigated through
- E.G.
Home / Learn / HTML / Navigationat the top of the page aria-label="breadcrumbs"attribute in nav- Use landmark
role="list"attribute in list - Don't link to the current page (bad UX for refresh) --> Denote using
aria-current="page"attribute
- E.G.
- Global Navigation: The global header that links to other top-level paths of the site
- Appears as the same nav on every page with
aria-current="page"on any links to the current page position="fixed"to affix to the top of the page (what aboutposition: "sticky"?)
- Appears as the same nav on every page with
Conditional Rendering
- e.g. Render on custom attribute
data-completeotherwisedisplay: none
.course .stack-nav a:not([data-complete="true"]) svg {
display: none;
}
Tables
Use tables for data that is being presented, compared, sorted, calculated or cross-referenced. Tables have a semantic meaning used by assistive technology for the aforementioned type of data.
- Alternative is to use lists styled with CSS; such as a grid of images if you want a neat layout
- Grid layout without data requiring tables: Use CSS grid
- Content in columns: Use multi-column layout
- Interactive slide deck explaining table elements
- Include aria
roleattributes when changing the CSS display property for table elements- Specify the
aria-sortattribute in HTML if table column is sortable
- Specify the
Table elements
<thead>Table head,<tbody>Table body and<tfoot>table footer<caption>captions are the preferred way of giving a name to a table<colgroup><col>or<tr><th><td>
Apply styles to entire columns
<colgroup>Defines groups of columns<col>grouped by<colgroup>
Define and style individual rows, header cells and data cells
- Each table row
<tr>contains one or more cells - Cell headers use
<th>, otherwise use<td><th>Header table cell: Usescope="col/row"attribute for accessibility
colspan/rowspanattribute: use to merge adjacent cells
Example table usage
| Name | Destiny | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Hal Gibrah | Calculator | 2020 |
| Cathy Terr | Waste disposal | 2018 |
| Lou Minious | Lightbulb | 1956 |
Images
- Should contain a
srcandaltattribute at a minimum- Alt descriptions should be short, assuming you are describing the image to somebody who cannot see it (using a screen reader)
- Responsive Images: Use
srcsetattribute to include multiple image sources with associated media queries- Provides multiple version based on resolution, sizes attribute and the browser viewport size
<picture>element: Equivalent to definingsrcset. Define sources with multiple<source>elements
- Set the
heightandwidthto avoid content layout shifts- These attributes will be overriden with CSS if setup correctly, however setting these attributes reserrves the space at the right aspect ratio and thus stops layout shifts
- Lazy loading with the
lazyattribute
Audio and Video
<video> Element:
- Elements to include inside the opening and closing tags
- Fallback content for what is loaded when the video fails
<soruce>Different sources can be specified (different media formats such as webm / ogg)- Formats specified by codecs parameter in
typeattribute ofsourceelement
- Formats specified by codecs parameter in
<tracks>defines captions tracks for subtitles inWebVTTformatkindattribute --> Specify "subtitles", "description" or "caption"- "caption" value should be reserved for transcription with sound effects and other relevant audio information
- Specify
srclangattribute with "subtitles" - "description" is for textual descriptions of the visual content
<poster>element: Image displayed as a still shot before the video is played
- Make sure to define the aspect ratio in HTML to avoid reflows & repaints (specify height and width)
- Background video: Typically use
autoplay loop muted role="none"attributes in video as these are not accessible (purely decorative videos)- Can improve performance by removing audio track from media sources
controlattribute adds media controls- Can override the browser's media controls
<audio> Element : Best for audio only
Templates, Slot and Shadow
Web Component standard: Use HTML templates, custom elements and the shadow DOM to build customized, encapsulated and reusable elements in HTML/JS
- HTML Templates:
<template>element used to declare fragments of HTML to be cloned and inserted into the DOM using Javascript- Contents of
<template>are not written to the screen <slot>Element allows you to inject your own markup into a template dynamically. Content inside the template will be distributed to the corresponding slot based on the slot names- The element within
<slot>will be replaced by the element matching the slot name if specified
- Contents of
<template id="star-rating-template">
<form>
<fieldset>
<slot name="star-rating-legend">
<legend>Rate your experience:</legend>
</slot>
...
<star-rating-template>
<star-rating-legend> ...replacement here </star-rating-legend>
</star-rating-template>
- Custom Elements: The process you register a defined HTML element with the browser
- Used to define new HTML elements with custom behaviour with JS
- Register with CustomElementRegistry.define()
- Requires name string, class that defines the behaviour, and optionally the parent class of the new element
- These are NOT replacements for Javascript component frameworks (think React components)
- Best practices for custom elements
- Shadow DOM: Allows hidden DOM trees to be attached to elements in the regular DOM tree
- CSS rules scoped to the regular DOM do not apply to the shadow DOM
- Shadow boundary: Boundary where the shadow DOM ends and the regular DOM begins
- Shadow DOM elements in a template can be edited with CSS using the
partattribute from the global scope
Example Web Component
- Note: the
<rating>element is undefined. - Undefined Elements: Treated by the browser as anonymous inline elements that can be styled with css
<template id="star-rating-template">
<form>
<fieldset>
<legend>Rate your experience:</legend>
<rating>
<input type="radio" name="rating" value="1" aria-label="1 star" required/>
<input type="radio" name="rating" value="2" aria-label="2 stars"/>
<input type="radio" name="rating" value="3" aria-label="3 stars"/>
<input type="radio" name="rating" value="4" aria-label="4 stars"/>
<input type="radio" name="rating" value="5" aria-label="5 stars"/>
</rating>
</fieldset>
<button type="reset">Reset</button>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</template>
Template defined can be drawn on the screen using the following JS by appending the contents of the <template> into the <body>
let starRating = document.getElementById("star-rating-template").content;
document.body.appendChild(starRating);
HTML APIs
What are HTML APIS? Manipulating the DOM using Javascript.
Example uses include:
- Getting the attribute values of an element like "alt"
- Getting the layout details like
HTMLElement.offsetHeightfor the height of a section in the webpage, or the orientation of a mobile user's screen - Getting the current UI state like mouse events or whether a video is playing
Pretty much every element has an associated DOM interface
Nodeinterface: Provides basic properties and methods inheried by all other DOM objects- Use to maintain the structure of a webpage by adding, removing or rearranging elements
Documentinterface: Represents entire web page and provides methods for creating, searching and manipulating elements- E.G.Query then attach event listeners to button click
HTMLDocumentinterface: Implementation of document interface that provides additional methods for HTML documents like metadata editing or setting the titleWindowinterface: Represents the browser window that contains the DOM document- E.G. Use for opening a new tab or popup
Elementinterface: Represents a single element in the DOM, use for like getting or setting attributes
Focus
tabindexattribute should be set so that tabbing visually moves through the page- Negative value makes element focusable but not tabbable
contenteditableattribute makes the element editable, tabbable and part of the tab orderdisabledattribute makes form controls unfocusable, and click events become voidinertattribute diables content and removes it from the accessibility tree
Inline Text Elements
Elements that provide text semantics for documentation
<code>element:Code examples<pre>element:Preformatted text<data>element: Machine readable translation 11000000<time>element: hasdatetimeattribute<sup>and<sub>super and subscript<kbd>: Keyboard input<dfn>: Definition
Text Emphasis:
<em>: Emphasises span of content<mark>: Highlight text such as marking the occurrence of search terms<strong>: Strong importance<cite>: Citation<i>: Used for technical terms, foreign words, etc. Italicizes text<u>: Content with non-textual annotation<b>: Draw attention to text with no semantic meaning<ruby>Container to hold annotations for other written languages
White Space:
<br>: Carriage return<hr>: Horizontal rule used as a separator<wbr>: Optionally break text if it overflows the container