ThreeJS
Build Tool: Use vite
Bundler:
Camera
Make sure the canvas' aspect ratio matches the camera!
PerspectiveCamera: Camera that renders with human perspective
- Field of View (vertical): 45-75 recommended
- Aspect ratio: width / height of the render
- Near and far: Range of lengths in which objects are rendered
- Don't use extremely small values to prevent z-fighting (gpu might not distinguish between extremely small distances)
- Defaults to 1, 1000
OrthographicCamera: Renders without perspective. Object is the same size regardless of distance to camera
- left, right, top, bottom: Distances in the direction you will render
- near and far
- You need to use the canvas ratio
const camera = new THREE.OrthographicCamera(- 1 * aspectRatio, 1 * aspectRatio, 1, - 1, 0.1, 100)to keep the same ratio of dimensions of the shape regardless of the aspect ratio- Canvas can stretch which will otherwise stretch the threejs projection
ArrayCamera: Render the scene from multiple cameras on specific areas of the render
StereoCamera: Two camera that mimic the eyes to create the parallex effect (use with VR)
CubeCamera: 6 Renders based on each face of the cube (used in environment maps --> reflections, shadows, etc.)
Types of Camera Controls
Can Listen on mousemove
- Don't forget to normalise mouse coordinates to [0, 1] or [-0.5, 0.5]
DeviceOrientationControls: Automatically retrieve the device orientation (useful for vr)
OrbitControls: Orbit an object in a spherical orbit
FlyControls: Fly around and rotate the camera
FirstPersonControls: Like FlyControl but with a fixed up axis
PointerLockControls: Uses pointer lock JS API (WASD first person)
- Makes the mouse disappear (use this as the FPS shooter camera)
TrackballControls: Like OrbitControls but without vertical angle limit
TransformControls: Let's you transform objects using AxesHelper. Let's you move objects around
Damping: Dampening the control movement to increase smoothness
- Check if controls has
enableDampingattribute
Other considerations:
- FOV adjustment
- Sensitivity
- Zoom levels
- Invert Y Axis
- Accessibility: Reduce camera shake, stable horizon, ^
Transform Objects
Four types of transform:
- position: Vector3
- scale: Vector3
- rotation: Euler --> Use radians.
- quarternion: Another way of representing rotations --> Avoids gimbal lock
Two ways of rotation:
- Updating
rotationorquarternionwill update the other property - The order of axes of rotation is important to avoid gimbal lock. Use
object.rotation.reordertoset the order axes are rotated - Gimbal Lock: Rotating on one axis changes the other axis orientation, causing two axes to align and causing the loss of rotation on one axis
Units are arbitrary. You decide what a unit represents
AxesHelper: Visualises the axis
lookAt(...)" Rotate an object's -z axis towards the target automatically/
- Useful for keeping the camera on an object
Group: Use to group objects together in the scene graph so transforms can be collectively applied to them
Geometries
Geometries are made of vertices, and can become either meshes (edges between vertices) or particles (each vertice is a particle).
Face: Triangle between three vertices used in a mesh.
Build-in ThreeJS Geometries: There are > 15 geometries
BufferGeometry: Core parent class of other geometries. Has a point in space with a position, UV coordinates, a normal and other attributes like colour or size.- PlaneGeometry: 2d plane
- TextGeometry: 3d text
Revisiting BoxGeometry:
- Width/Height/Depth Segments: Number of segmented rectangular faces along the sides
- Subdivision: Refers to the process of refining the complexity of a geometric shape by adding more vertices
How do you create your own geometry?
Float32Array: Define x, y, z for each vertice- Convert to
BufferAttribute(arr, itemSize): Stores data for an attribute associated withBufferGeometry - Add the
BufferAttributeto your meshBufferGeometryusingsetAttribute("position", yourBufferAttribute)."position"is an attribute used by the built-in ThreeJS shaders
Performance considerations:
- Used indexes on your
BufferGeometryto reuse vertices
Animations
Window: requestAnimationFrame() method: Tell the browser you want to update an animation. The browser paints the animationin the next repaint / frame.
- Call this at the end of the animation loop / tick function
GSAP: Javascript animation framework for the web
Textures
An image is a 2D picture designed to be viewed by a human.
A texture is specially prepared data used for various purposes in 3D graphics.
- The points that make up a texture are called texels
Types of texture map:
- Color/Diffuse/Albedo: Colour map applied on the geometry
- Alpha: Opacity map
- Height/Displacement: Adds surface details
- Normal: For shiny surfaces
- Ambied Occlusion: Fake shadows for more detail
- Metalness: Used for reflective surfaces
- Roughness: Light dissipation, often related to metalness
Physics Based Rendering (PBR)
How do you load textures?
- Create a
TextureLoader(optionally with aLoadingManager)
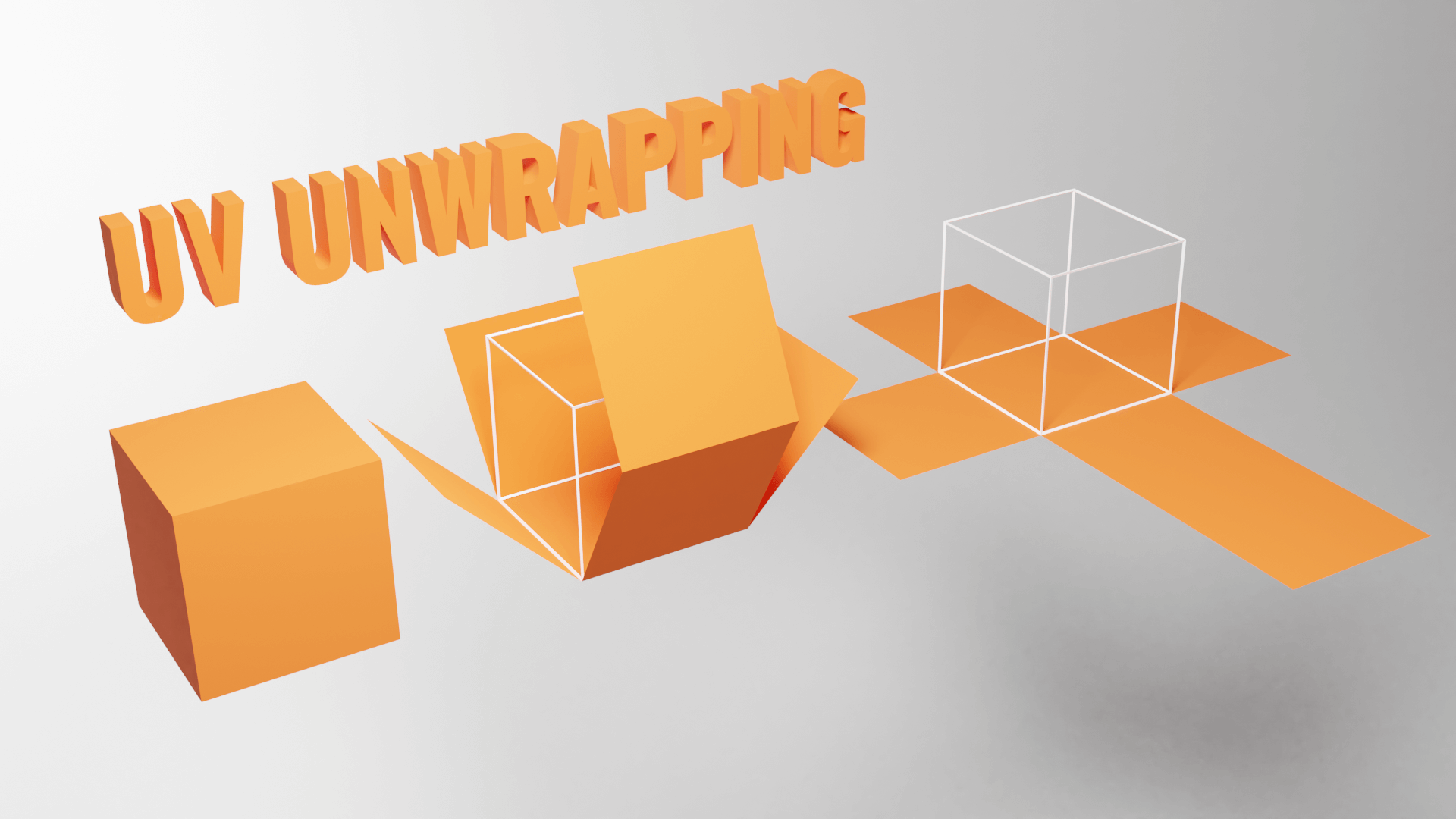
UV Mapping: How 2D textures are placed on 3D geometries
- (u,v)⟶(x,y,z)
Texture transformations: Properties on textures
- repeat: Repeats the texture by setting (wrapS and wrapT attributes for x, y wrapping)
colorTexture.repeat,colorTexture.wrapS,colorTexture.wrapT
- Offset: Offset UV coordinates of a texture
- Rotation: Rotate a texture around the pivot point (defaults to bottom left)
- Change the pivot point with
center
- Change the pivot point with
Filtering: When textures are too close or too far, we can have visual artifacts that reduce the quality of the texture
- Mipmapping: Technique of creating smaller versions of the texture, so the GPU can choose the most appropriate texture
- Texture size needs to be divisible by 2
- Filters applied by ThreeJS
- Minification Filter: The minification filter happens when the pixels of texture are smaller than the pixels of the render. In other words, the texture is too big for the surface, it covers.
- THREE.NearestFilter
- THREE.LinearFilter
- THREE.NearestMipmapNearestFilter
- THREE.NearestMipmapLinearFilter
- THREE.LinearMipmapNearestFilter
- THREE.LinearMipmapLinearFilter
- Magnification Filter:The magnification filter works just like the minification filter, but when the pixels of the texture are bigger than the render's pixels. In other words, the texture too small for the surface it covers.
- THREE.NearestFilter: best for performance
- THREE.LinearFilter
- Minification Filter: The minification filter happens when the pixels of texture are smaller than the pixels of the render. In other words, the texture is too big for the surface, it covers.
Optimizing textures:
- Use sizes divisible by 2
.jpg: Lossy but lighter (better for web generally).png: Lossless but heavier- Supports transparency (alpha) whilst JPEG doesn't
Basis: Small file, optimised for GPU
Where to find textures? Consider:
- poliigon.com
- 3dtextures.me
- arroway-textures.ch
Fullscreen Applications
Remove margin around the canvas and fix the position
html,
body
{
overflow: hidden;
}
.yourWebGLCanvas
{
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
outline: none;
}
Add event listener fo resize
window.addEventListener('resize', () =>
{
// Update sizes
sizes.width = window.innerWidth
sizes.height = window.innerHeight
// Update camera
camera.aspect = sizes.width / sizes.height
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
// Update renderer
renderer.setSize(sizes.width, sizes.height)
renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(2, window.devicePixelRatio))
})
Pixel Ratio: Physical to logical pixel mapping
- Can cause jaggies (stair stepped edges)
- Jaggies are prevented through optimal compression, vector graphics or anti-aliasing
- To handle pixel ratio, use
renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(2, window.devicePixelRatio))in the resize event- Humans can't see pixel ratios > 2. Do this to prevent unnecessary pixel colourings
- Used when you move the window between screens with different resolutions
Going fullscreen: canvas.requestFullscreen()
- exit:
document.exitFullscreen()
// Can change the event to whatever you want to go fullscreen
window.addEventListener('dblclick', () =>
{
if(!document.fullscreenElement)
{
canvas.requestFullscreen()
}
else
{
document.exitFullscreen()
}
})
Debuggers
Example Debuggers
- dat.GUI (lil-gui because vulnerabilities)
- control-panel
- ControlKit
- Uil
- Tweakpane
- Guify
- Oui
lil-gui:
import GUI from 'lil-gui'
const gui = new GUI();
// Add GUI value in range
gui.add(yourObject, "yourAttribute").min(-10).max(10).step(0.01)
// Example gui state obj
const parameters = {
color: 0xff0000,
spin: () =>
{
gsap.to(mesh.rotation, { duration: 1, y: mesh.rotation.y + Math.PI * 2 })
}
}
// Change values
gui
.addColor(parameters, 'color')
.onChange(() =>
{
material.color.set(parameters.color)
})
gui.add(parameters, 'spin')